K. Kamatchi1, Rajesh Kumar.N.T2, Kandhasamy.S3
Corresponding Author:
1Assistant Professor, Faculty of Physiotherapy, A.C.S. Medical College and Hospital Campus, DR. MGR. Educational and Research Institute, Deemed to be University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Mail Id: kamatchi.physio@drmgrdu.ac.in
Co-Authors:
2, 3 MPT Students, Faculty of Physiotherapy, A.C.S. Medical College and Hospital Campus, DR. MGR. Educational and Research Institute, Deemed to be University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
| ABSTRACT |
Background: Varicose veins are torturous, widened superficial veins in the subcutaneous tissues of the legs which are often easily visible these are generally larger than 3mm in size. According to the population in India patients with varicose veins in India is about 15-20% of populations and is increasing day by day. Objective of the study is to find the effectiveness of aerobic exercise versus Buerger’s exercise in varicose vein among security guards.
Methodology: This is a comparative study with 30 patients of the security guards from A.C.S. Medical College and Hospital. The inclusion criteria will be both males and females with the age group of 35 to 55 years and the patients having grade 2 oedema. In this study group A consists of 15 patients was trained with aerobic exercise training and group B consists of 15 patients was trained with Buerger’s exercises. Aerobic exercise was performed for 30 minutes per day for four sessions in a week and this was given for 12 weeks and Buerger’s exercises was performed for 30 minutes per day for four session in a week and this was given for 12 weeks. The pre and post-test values were compared using the VAS (visual analogous scale), 6- minute walk test.
Result: On comparing Pre test and Post test within Group A& Group B on Visual Analog Scale & 6 Minute Walk Test score showed highly significant difference in Mean values at P ≤ 0.001 but buerger’s exercise is more effective than aerobic exercise.
| Conclusion: Buerger’s exercise is more effective on reducing varicose vein among security guards |
Keywords: Varicose vein; Aerobic exercise; Buerger’s exercise.
| Received on 29thJanuary 2022, Revised on 19thFebruary 2022, Accepted on 26thFebruary 2022, DOI:10.36678/IJMAES.2022.V08I01.005 |
INTRODUCTION
Generally, the leg veins have one-way valve in them so that muscle contract them and blood can go only in one direction this up the leg which are seen in normal veins.Due to which there is failure of valves to close properly and allows in both directions. This backward flow of blood is known as venous reflex 1,2.
Due to this there is accumulation of blood in legs causing varicose veins. Varicose veins are torturous, widened superficial veins in the subcutaneous tissues of the legs which are often easily visible. Varicose veins are among the most common chronic conditions seen by physicians today. A varicose vein, sometimes called varicosity occurs when a valve weakness putting more pressure on the other valves and causing blood to stagnate 3, 4.
There are generally larger than 3mm in size located on the size of the calf muscles.Varicose veins are preventable. Maintaining healthy body weight and doing exercises help lessen their emergence appropriate exercise can be the best preventive and defensive strategies against varicose veins 5.
Any program of regular exercises circulation improves muscle tone and helps prevent varicosities. However, high-impact aerobics, jogging, strenuous cycling, or any intense activity may increase blood pressure in the legs and accentuate varicose vein. Walking is the great exercise for the lower leg area–either out in the open or in a treadmill especially with the incline level simple intervention like leg elevation, water immersion and exercise should be studied6,7.
The mechanism of Buerger’s exercises use gravitational changes in positions that are applied to smooth musculature of vessels and to vascular 8. Gravity helps alternate to empty and fill blood columns, which can eventually increase transportation of blood through them9.
The exercises involve the individual lying flat in bed with the legs elevated at 45 degrees until blanching occurs or for a maximum of 2 minutes. The patient then sits on the edge of the bed with the feet hanging down. Further exercise includes dorsiflex, plantarflex, then inward and outward movements of the feet, followed by flexing and extending the toes 10, 11.
Before and after World War 2 medical experts did not know how to operate or treat the patient suffering from atherosclerosis or vessel occlusion, as well as stiffening in their peripheral arteries. Some medical genius at that time developed postural treatment to improve circulation in the lower extremities12-15.
Aim & Need of the Study: Varicose veins are torturous, widened superficial veins in the subcutaneous tissues of the legs which are often easily visible these are generally larger than 3mm in size. They are usually enlarged and are located on the inside of the calf muscles. Varicose veins are more common seen in women than men. According to the population in India patients with varicose veins in India is about 15-20% of populations and is increasing day by day. This study aims to find the comparative effect between buerger’s exercise and aerobic exercise.
Hence the need of the study is to find the effectiveness of aerobic exercise versus Buerger’s exercise in varicose vein among security guards.
This was an experimental comparative study pre and post study conducted at ACS Medical College and hospital Chennai. Total 30 patients were selected for this study; they were security guard in ACS College. The study conducted for study duration of 3 months. Inclusion criteria for the study were both male and female aged between 35 to 55 years; Patients were clinically diagnosed with varicose vein with edema grade 2. Patient with deep vein thrombosis, recent lower limb fracture, uncooperative subjects, any neuropathies or ulcers in lower limb, patients undergone with recent lung surgical intervention in lower limb were excluded from this study. Outcome measures for the study were VAS (Visual Analog Scale) and 6 min walk test
Procedure: The patients who fulfill the inclusion criteria were included in the study. The consent was obtained from the patient and the assessment was done and they were divided into two groups each group having 15 patients. Group A patients received aerobic exercise. Group B received Buerger’s exercise. Both groups received treatment duration for 4 sessions in a week up to 12 week after 12 weeks the patients was assessed by pre and post values of VAS scale and 6 minutes’ walk test.
Aerobic exercises
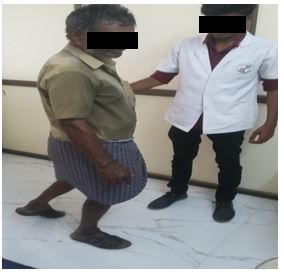
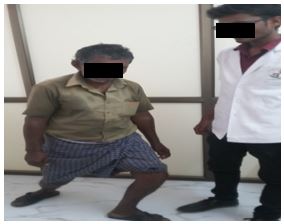
Walking or running: Walking just 20 minutes a day and running minimize the stress on your joint.
Bicycle legs: 5 minutes riding a bicycle or lying on back put legs in the air, bending them at knee. Pedal them slowly either leg at once or alternate one at a time.
Lunges: 5 minutes stand with legs apart. Step forward slow bending knee and make sure to keep knee directly above the ankle hold it then slowly straighten the leg and step back to original position, repeat with the other leg. While standing with Leg straight, rise up on tip toes and then lower back down.
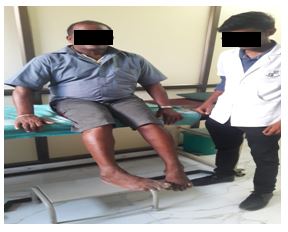
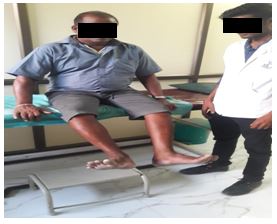
Buerger’s exercise: Buerger Allen exercise- specific exercises intended to improve circulation to the feet and legs. The lower extremities are elevated to a 45 to 90 degree angle and supported in this position until the skin blanches (appears dead white). The feet and legs are then lowered below the level of the rest of the body until redness appears (care should be taken that there is no pressure against the back of the knees); finally the legs placed on the bed for few minutes.
The length of the time for each position varies with the patient’s tolerance and the speed with which colour change occurs. Usually the exercises are prescribed so that the legs are elevated for 2 to 3 minutes, down 5 to 10 minutes and then flat on the bed for 10 minutes.
- Aerobic exercises

- Buerger’s Exercise
Data Analysis: The collected data were tabulated and analyzed using both descriptive and inferential statistics. All the parameters were assessed using statistical package for social science (SPSS) version 24.
Paired t-test was adopted to find the statistical difference within the groups & Independent t-test (Student t-Test) was adopted to find statistical difference between the groups.
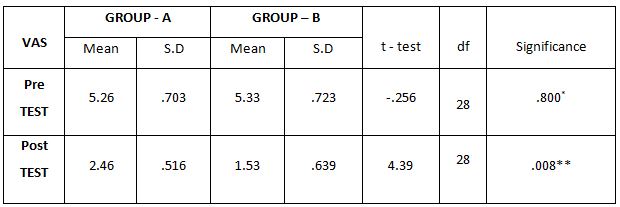
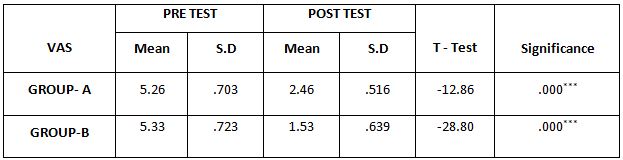
Table-1. Comparison of Visual Analog Scale Score between Group – A and Group – B in Pre and Post Test
The above table reveals the Mean, Standard Deviation (S.D), t-test, degree of freedom(df) and p-value between (Group A) & (Group B) in pre test and post test weeks.
This table shows that statistically significant difference in post test values between Group A& Group B (**- P ≤ 0.05)
This table shows that there is no significant difference in pre test values between Group A& Group B (*P > 0.05).
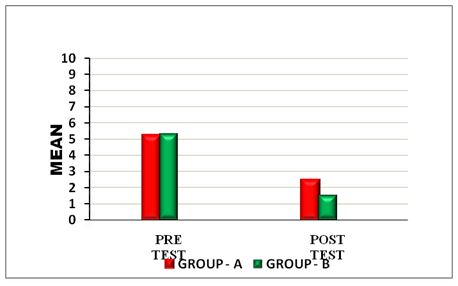
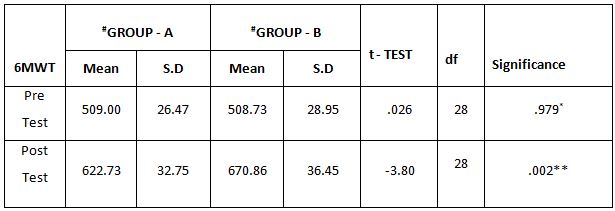
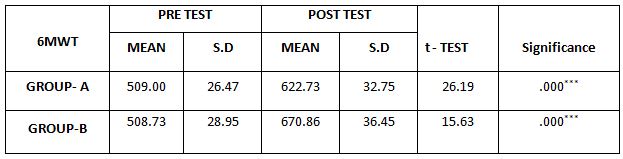
Table-2. Comparison of 6 Minute Walk Test between Group – A and Group – B in Pre and Post Test
The above table reveals the Mean, Standard Deviation (S.D), t-test, degree of freedom(df) and p-value between (Group A) & (Group B) in pre test and post test weeks.
This table shows that there is no significant difference in pre test values between Group A& Group B (*P > 0.05). This table shows that
statistically significant difference in posttest values between Group A& Group B (**- P ≤ 0.05)
The above table reveals the Mean, Standard Deviation (S.D), t-value and p-value between pre-test and post-test within Group – A &Group – B. There is a statistically highly significant difference between the pre test and post test values within Group A and Group B(***- P ≤ 0.001).
The above table reveals the Mean, Standard Deviation (S.D), t-value and p-value between pre-test and post-test within Group – A &Group – B.
There is a statistically highly significant difference between the pre test and post test values within Group A and Group B(***- P ≤ 0.001).
RESULTS
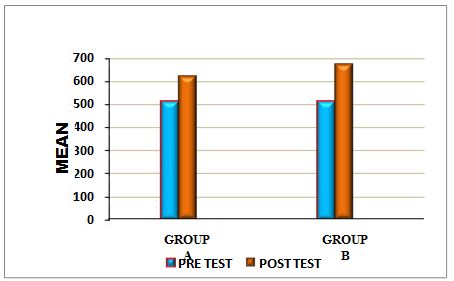
On comparing the Mean values of Group A & Group B on Visual Analog Scale Score, both the groups showed significant decrease in the post test Mean values, but (Group B – Buerger’s Exercise) shows 1.53 which has the Lower Mean value is effective than (Group A -Aerobic Exercise) 2.46 at P ≤ 0.05. Hence Null Hypothesis is rejected.
On comparing the Mean values of Group A & Group B on 6 Minute Walk Test Score, both the groups showed significant increase in the post test Mean values but (Group B – Buerger’s Exercise) shows 670.86 seconds which has the Higher Mean value is effective than (Group A -Aerobic Exercise) 622.73 , secondsat P ≤ 0.05. Hence Null Hypothesis is rejected.
On comparing Pre test and Post test within Group A& Group B on Visual Analog Scale & 6 Minute Walk Test score showed highly significant difference in Mean values at P ≤ 0.001
DISCUSSION
The purpose of this study is to find out the comparative effect between aerobic exercises versus Buerger’s exercise in varicose veins. Varicose veins are torturous, widened superficial veins in subcutaneous tissues of the legs which are often visible.
The study was carried out and the result was drawn by using vas scale and 6-minute walk test as the outcome measure. 30 patients diagnosed as varicose veins the age group between 35- 55 years. Study place was ACS Medical College and hospital, Chennai. The patients are evaluated and divided into two groups. Group A included 15 subjects treated with aerobic exercise and Group B included 15 subjects treated with Buerger’s exercise. In the present study
When comparing the Mean values of Group A & Group B on Visual Analog Scale Score, both the groups showed significant decrease in the post test Mean values, but (Group B – Buerger’s Exercise) shows 1.53 which has the Lower Mean value is effective than (Group A -Aerobic Exercise) 2.46 at P ≤ 0.05.
When comparing the Mean values of Group A & Group B on 6 Minute Walk Test Score, both the groups showed significant increase in the post test Mean values but (Group B-Buerger’s Exercise) shows 670.86 seconds which has the Higher Mean value is effective than (Group A -Aerobic Exercise) 622.73 seconds at P ≤ 0.05.
On the comparing the pre and post values by VAS (visual analogous scale) and 6 minute walk test both the exercises shows significant results but buerger’s is more effective than aerobic exercise. Evidence of similarly enhanced buerger’s exercise has been found in the previous studies.
Jian Wei-Ya, et al. (2009) compared with conventional rehabilitation training, buerger’s exercise was more effective in reducing the post –surgery pain asd swelling of patients with the lower limb fractures.
Chyong Fang Chang Rn, MSN et al. (2015) showed that buerger’s exercise combined with the health promoting program significantly improved among community residents at high risk for diabetic foot ulceration.
Poonam Thakur, et al. (2019) proved that buerger’s exercise is improving peripheral circulation among patients with diabetes mellitus admitted in sharda hospital at Noida.
Chyong Fang Chang, et al. (2015) found that buerger’s exercise benefits for PAOD patient’s post- operative patients with orthopaedics and gynaecology problems by improving local circulation.
Ethical clearance: There was no risk of conducting this study.Ethical clearance was obtained from the ethical Institutional Review Board of Faculty of Physiotherapy, Dr. MGR. Educational and Research Institute, Chennai with reference No. A43/PHYSIO/IRB/2018-2019 approval letter dated 07/01/2019.
Conflicts of Interest: There is no conflict of interest to conduct this study.
Fund for the study: This is self-funded study.
CONCLUSION
The present study concluded that both exercise showed a significant results but Buerger’s exercise is more effective than aerobic exercise.
REFERENCES
1. Clendo J A, child J D, stowell T et al., immediate effects thoracic manipulation in patients with neck pain: a randomized clinical trial. Man ther. 2005 May; 10(2); 127-35.
2. Conley MS, mayor RA, Bloomberg JJ, et al., non-invasive analysis of human neck muscle function. Spinc, 1995, 20; 2505-2512.
3. Ariens GA, bongers PM, Dowes M, et al., Are neck flexion, neck rotation, and sitting at work risk factor for neck pain? Occup environ med, 2001; 58; 200-207.
4. Haldemen S, carrol L, Cassidy JD, et al. Finding from bone and joint decade 2000-2010 task force on neck pain andits associated disorders. J Occup Environ med. 2010; Apr: 52(4); 424-7.
5. Janda V; muscles and motor control in cervicogenic disorder: assessment and management. In: physical therapy of the cervical and thoracic spine. 2nd ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1994; pp. 195-216
6. Jull GA, falla DL et al. Clinical assessment of the deep cervical flexor muscles; the craniocervical flexion test. J manipulative physio ther. 2008 Sep.; 31(7); 525-33.
7. Jhohans blomgren et al., effects of deep cervical flexor training on impaired physiological functions associated functions with chronic neck pain: a systematic review. BMC musculoskeletal disorders 2018, 19:415.
8. Sinho Chung et al. Effects of the cranio cervical flexion and isometric neck exercise compared in patients with neck pain: A randomized controlled trail. Physiotherapy theory and practice, 2018:1-10.
9. Stretching Exercises to Prevent Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders – A Review Article; Journal of Sports Science & Medicine, May 2017; 5(2):27-37.
10. Mohammed Ali et al. the effects of different exercise programs on size and function of deep cervical flexor muscles in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain: A systematic review of randomized. American journal of physical of physical medicine & rehabilitation, 2017; 96(8); 582-588.
11. Jin young Kim et al., Clinical effects deep cervical muscular activation in patients with chronic neck pain. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016; 28; 269-273.
12. Akbari Asghar et al., investing the effects of stabilization exercise and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation exercise on cross-sectional area of deep cervical flexor muscles in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain. International journal of medical research &health science, 2016; 11; 502-508.
13. Amira hussian draz et al., efficacy of deep cervical flexor exercise for neck pain: a randomized controlled study. Turk J phys med rehab., 2016; 62(2); 107-115.
14. Eun young Kim et al., comparison of the effects deep cervical flexor strengthening and Mackenzie neck exercises on head forward postures due to the use of smart phones .Indian journal of science and technology, April 2015; Vol.8(S7); 567-575.
15. Dong yeon kang et al., deep cervical flexor training with a pressure biofeedback unit is an effective method for maintaining neck mobility and muscular endurance in college students with forward head posture. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015; 27; 3207-3210.
16. Zaheen Ahmed iqbal et al., Flexor training using pressure biofeedback on pain and disability of school teachers with neck pain. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013,25; 657-661.
17. Nezamuddin, MD., et al., Efficacy of pressure biofeedback guided deep cervical flexor training on neck pain and muscle performance in visual display terminal operators. Journal of musculoskeletal research. 2013; Vol. 16; No.03; 1350011.
18. Saad Ammar Al-Harbi, et al., compare the effects of deep cervical flexor strengthening exercises verses electrotherapy modalities on head forward postures resulting from the use of smart phones. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2013; Volume 6; Issue 6; 266-277.
19. Petri salo et al., neck muscle strength and mobility of the cervical spine as predictors of neck pain: a prospective 6-year study, 2012; Spine 37(12); 1036-1040.
20. Takala ep et al., active neck muscle training in the treatment of chronic neck pain in women: A randomizes controlled trial .jama.2003 may 21; 289(19): 2509-16.
21. Geoffrey R. Williams et al., colony collapse disorder in context. Trends Ecol. 2012; Vol 20; 367-72.
22. Falla et al., the change in deep cervical flexor activity after training is associated with the degree of pain reduction in patients with chronic neck pain. Clin. J. Pain, 2012; 28 (7); 628-634.
23. Aquino RL, et al., applying joint mobilization at different cervical vertebral levels does influence immediate pain reduction in patiets with chronic neck pain. J Man Manip Ther. 2009; 17(2):95-100.
24. Luch E, et al., effects of deep cervical flexor training on pressure pain thresholds over myofacial trigger points in patients with chronic neck pain. J Manipulativ Physiol Ther. 2013 Nov-Dec; 36(9): 604-11.
| Citation: K. Kamatchi, Rajesh Kumar.N.T, Kandhasamy.S. A comparitive study to analyse the effectiveness of aerobic exercise versus Buerger’s exercise in varicose vein among security guards, International Journal of Medical and Exercise Science, March 2022; 8(1); 1199-1209. |


Leave a Reply