Changes in eating habits among youth: A study on college students in Chennai City
LEENA VS1*, LAZAR.S2, JIBI PAUL1
ABSTRACT
Back ground of the study: As the adolescence grows the food habits also changes accordingly. Eating healthy food promotes good healthy development among the young citizen called youth. Physical, mental, emotional and social behaviors also get altered due to the junk food habit. This study was aimed to examine the extent which the youth seek junk food, reasons for this craving among youth, impact of junk food eating habit and to study the efforts made to respond the problem of obesity.
Methodology: Exploratory research design with the aims to establish the most basic criteria of the research topic, often before the actual study was started. Convenient sampling method was used for different group of samples. Seventy (70) subjects were participated in the study. Samples selected from college students of 2 different cities in Chennai; Nungambakkam and Avadi. Validated questionnaire were used to find the outcome of the study.
Result: Many responded that the junk food is a solid food it is clearly found with the ratio (65.71%), many finding were observed that the junk food culture and that changes in eating pattern.
Conclusion: The complex and evolving nature of youth attitudes towards obesity prevention efforts and their understanding of the causes and consequences of obesity.
Keywords: Junk food habit, good health, social behaviors, obesity
Received on 11thNovember 2018, Revised on 22nd November 2018, Accepted on 28th November 2018
INTRODUCTION
As the adolescence grows the food habits also changes accordingly. Eating healthy food promotes good healthy development among the young citizen called youth. Physical, mental, emotional and social behaviors also get altered due to the junk food habit 1, 2.
According to a Swedish study published in the journal of the American college of cardiology four out of five heart attacks can be prevented by following 5 healthy behaviors, maintain healthy weight and diet (avoiding junk and packed foods), exercising, not smoking and moderating alcohol use. But they don’t remember that they are eating slow poison to put themselves into risk and this junk food habit is 89.9% prominent among college youths according to many studies done by nutritionists3, 4.
National survey suggested that the physical activity and fitness level is declining due to this junk food habits in 1950. The importance of fat was studied by Prof. Ancel Keys in the seven nations study, where keys and co-workers found that Finland and UK had high coronary heart disease (CHD) compared to this the problem is in low level in Japan and Greece (Crete).
In 2000, the sub-committee on nutrition of the United Nation (UN) produced another major statement with the 4th report on the by world nutrition situation. Nutrition throughout the life-cycle, these reports proposed that trends in global diet-first noted in affluent societies but emerging in developing societies-are followed by the emergence of clear patterns of chronic disease, particularly Cardio Vascular Disease (Coronary Heart Disease, High Blood Pressure, and cerebro-vascular Disease), some Cancers(Stomach, Colorectal, Breast, Prostrate and so on), Diabetes, Obesity 5, 6, 7.
According to WHO in 2005 there were about 1.6 billion overweight person aged 15 years and above and among them at least 400 million adults were obese. As a resultant of this food culture there is an increased level higher prevalence of 1.7 billion people classified as overweight 8, 9.
Objectives of the study: This study was aimed to examine the extent which the youth seek junk food, reasons for this craving among youth, impact of junk food eating habit and to study the efforts made to respond the problem of obesity.
MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY
Research study setting: This study was conducted at Loyola College, Veltech College Chennai. Loyola College is a Jesuit institution. Rev. Fr. Francis Bertram and a band dedicated Jesuits, who came over to Chennai at the invitation of the most Rev. Dr.J.Aelen, Archbishop of Chennai to open a catholic college for young men in the state capital, founded it. It is an Autonomous College, The name Loyola comes from the ancestral castle where Saint Ignatius of Loyola was born in 1491, the last of a large Basque family. Veltech College Under the guidance of Directorate of Technical Education this college was started in the year 1998 with 4 branches. They have dedicated team of academicians with whose support students score University Medals and Ranks.
Exploratory Research Designused to conduct this study. Convenient Sampling method used to select the samples for the study. Total 70 samples were selected from Veltech College and Loyola College students of 2 different cities in Chennai, Nungambakkam and Avadi.
Study Instruments: Validated questionnaire used for obtaining statistically useful personal information from the individuals.
RESULT
Demographic analysis of junk food habit respondent from age 17-35 years were chosen in that 23-years old were higher in ratio following that 22-years,21-years and 20-years, the junk culture among college student is more among the age 23years and the value is calculated giving 100% for 70 samples.
The ratio of respondence was from the male side that is 65.71% and in female 34.28% and the changes in eating habit was more among the male students (Table 1).
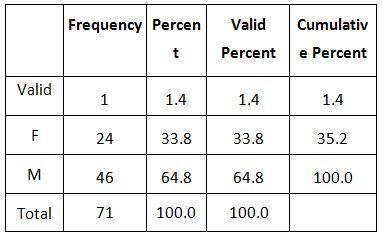
Many responded that the junk food is a solid food it is clearly found with the ratio (65.71%), many finding were observed that the junk food culture and that changes in eating pattern.
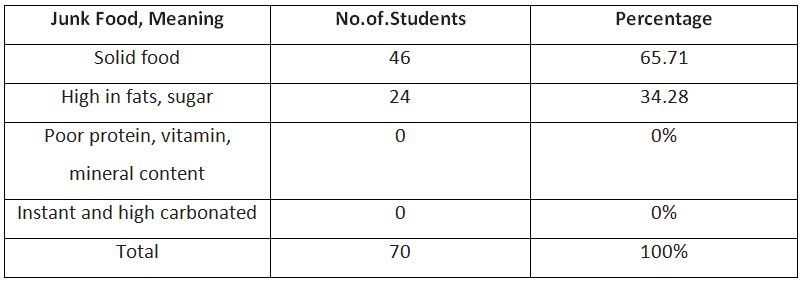
From the above data (Table.2) it is analyzed that most of the student’s idea on junk food is known as a solid food and high in fat, sugar. It is to understand in a clear cut that this is scientifically proved by Mr. Michael F. Jacobson in 1972 in the research on center for science and public interest and also from the sample survey it is proved that 65.71% of students believe junk food as a solid food and 34.28% of students believe it as food that is high in fats, sugar. But the students are not aware that it is also poor in protein, vitamin and minerals content and also instead highly carbonated.
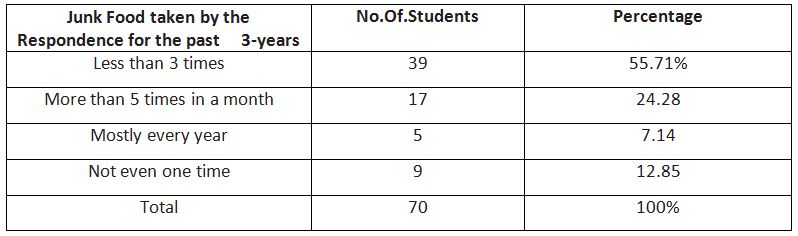
From the Table3 it has been viewed that for the past 3-years many had pizza, burgers and fries less than 3-times from this data it is clearly understood that many youth get into the habit
and eating pizza, burgers and fries, 55.71% of youth chosen less than three times, 24.28% more than 5-times in a month, 12.85% not even on time and 7.14%.
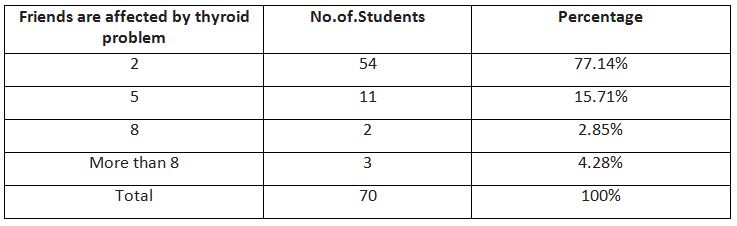
In Table 5, It is observed that 77.14% of youth are affected by the thyroid problem which is leading more among females and males, 54% of the respondents friends (2), 15.71% of the respondents friends ratio affected by thyroid (5), 2.85% of the respondents friends ratio (8), 4.28% of the respondents friends ratio (more than 8).It is identified every fourth person in a youth crew have the complexity of thyroid problem that is of ratio 1:4.
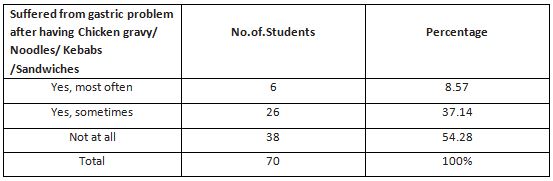
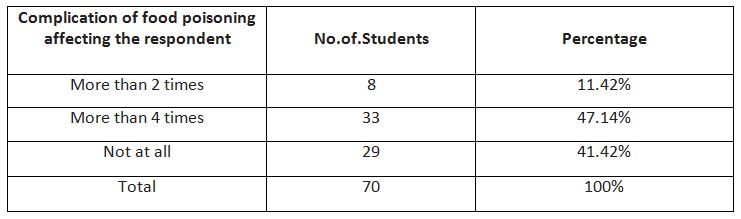
According to Table 6,it is understood that gastric problem after eating chicken gravy or noodles or kebab’s or sandwiches affected 8.57% of the students most often, 37.14% sometimes, 54.28% not at all. Since this cause an intestinal problem which affects the digestive system.
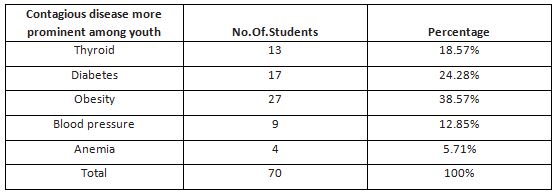
From the Table 7,the most contagious disease prominent among youth in presence scenario was 13% thyroid, 17% diabetes, 27% obesity, 9% BP high or low, 4% anemia. But the real fact is obesity, thyroid and anemia playing its role in this food habit. This is the main problem caused more among the youths and this is actually an initial problem but which gets complicated due to the junk food habits which the youths follow is highly dangerous.
DISCUSSION
Mr.Ardith R, Mr.Brunt and Mr.Yeong S. Rhee (2008) studied on “Obesity and Lifestyle in U.S. College students related to living arrangements”, Where the objectives on the influence of dietary variety and other behaviors among American College students. The samples were primarily white of traditional college age, and primarily female, and the sample size were 738 surveys and participants returned were 585 (79%) 10.
The junk food culture and the bad lifestyle is more prominent among the off-campus students that is who stays away from family, this result is accepted but even though the youth who is staying with family is also prone to this junk food culture and spoiling their health in additional to this argument there is another review placed by Dr. Melody Y. Knight, Dr.Lorraine Killion, Dr.Larry P. Knight (1st Jan 2014), studied on the “Nutrition, Exercise habits, and perception of Obesity in Hispanic College Students in South Texas: A 10 years follow up”, Where the objective was to determine whether Hispanic College Students perceive themselves to be more Overweight than other ethnicity and to find out the diet practice, lack of exercise and also both categories 11.
Mr. Goel S, Mr. Karur T and Mr.Gupta M (March 2013) researched on “Increasing Proclivity for Junk Food among Overweight Adolescent Girls in District Kurukshetra, India”, the study progressed in such a way that in obesity in adolescents in gradually becoming a major public health problem in many developing countries, including India. Being overweight as an adolescent is associated with being overweight as an adult, the objective was change in dietary habit of consuming more high energy junk food and shifting to sedentary lifestyle is likely to be one of the important precursors of overweight and obesity among adolescent 12.
Research study on the college students food habits connecting with case study was done by Ms. S. Steffi and Ms. R Mary Josephine (Jan-Mar 2013),”A Case Study on Trend of Food Style among College Students”, this study was undertaken to explore the trend of having food related lifestyle among the college students, objective was to identify the Socio-Demographic characteristics and investigate the difference in attitude towards fast food, junk food and normal food 13.
CONCLUSION
Obesity is now accepted and acknowledged as a problem amongst youth and by youth. However, attitudes towards prevention of obesity through employment of healthier habits remain mixed, with primarily negative connotations around healthy lifestyle choices. It is well documented that excessive caloric intake and inadequate physical activity are important contributors to weight gain and obesity. Study suggests that youth may benefit from education designed to increase the desirability of healthy habits, either from gaining benefit or from avoiding consequences, specifically linking lifestyle choices with weight-related outcomes.
Limitation of the study: Lack of time to analyze complexity of disease was the main problem. More sample size would have been done for broader outcome of this survey.
Recommendation: More research can be done on the eating habit and complication caused by the eating habit to youth, the infertility problem occurring due to junk food culture can be researched and the major complexity in brain signaling and body metabolism can be researched.
Acknowledgement: I am greatly indebted to Dr. Rabindran’s Health Care Center, Ambathur OT, Chennai for allowing me and my team to access the hospital premises and interact with the staff. I would like to extend my gratitude to Dr. R. N. Baba (MD), Dr. Revathy Baba (Director) and Mr. Pradeep(HR), and also my special hearty thanks to Dr. Kopuram Devi who helped me and gave lots of information related to my research and also helped to collect data. I would like to thank each and every staff members of each department especially insurance department staffs and front office for giving me the details for my research. Next, I would like to thank my guide Dr.S.Lazar.SJ who molded me to present a neat and best work in all perspective. He gave ideas and encouraged me to perform best.
REFERENCES
- Lawrence, D., Schank, M.J. (1993). Health status, health perceptions and health behaviors of young adult women. International Journal of Nursing Studies.30, 527-535.
- Haberman, S., Luffey, D. (1998).Weighing in college students’ diet and exercise behaviors. Journal of American College Health.46, 189-91.
- Gow, R.W., Trace, S.E., Mazzeo, S.E. (2010) Preventing weight gain in first year college students: An online intervention to prevent the “freshman fifteen”. Eating Behavior. 11(1), 33-39.
- Despues, D., Friedman, H. (2007) Ethnic differences in health behaviors among college students. Journal of Applied Social Psychology. 37(1), 131-142.
- Douglas, K.A., Collins, J.L., Warren, C. (1997). Results from the 1995 National College Health Risk Behavior Survey.Journal of American College Health. 46,55-66.
- Ogden, C.L., Flegal, K.M., Carroll, M.D., Johnson, C.L.(2002). Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999-2000.Journal of the American Medical Association.286, 1728-1732.
- Huang, T.K., Harris, K.J., Lee, R.E., Nazir, R., Born, W., Kaur, H. (2010). Assessing overweight, obesity, diet, and physical activity in college students.Journal of American College Health. 52(2), 83-86.
- Irazusta, A., Hoyos, I., Irazusta, J., Ruiz, F., Biaz, E., Gil, J. (2007). Increased cardiovascular risk associated with poor nutritional habits in first-year students. Nutrition Research.27, 387-394.
- Grinnell, S., Breene, G., Melanson, K., Blissmer, B., Lofgren, I. (2011). Anthropometric and behavioral measures related to mindfulness in college students. Journal of American College Health. 59(6), 539-545.
- Hensley, T. (1999). Obesity epidemic increases dramatically in the United States: CDC Director calls for National Prevention Effort.CDC, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention & Health Promotion. (770), 488-5820.
- Boyle, J.R., LaRose, N.R. (2008). Personal beliefs, the environment and college students’ exercise and eating behaviors.American Journal of Health Studies. 23(4), 195-200.
- Brevard, P.B., Ricketts, C.D. (1996). Residence of college students affects dietary intake, physical activity, and serum lipid levels. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 96, 35-38.
- Flegal, K.M., Carrol, M.D., Ogden, C.L., Curtin, L.R. (2010) Prevalence and trends in obesity among U.S. adults, 1999-2008. Journal of the American Medical Association. 303, 235-241.
| Citation: |
Leena V S, Lazar.S, Jibi Paul (2018).Changes in eating habits among youth: a study on college students in chennai city, ijmaes, 2018, 4(4), 510-517.
